Homoscedasticity and heteroscedasticity
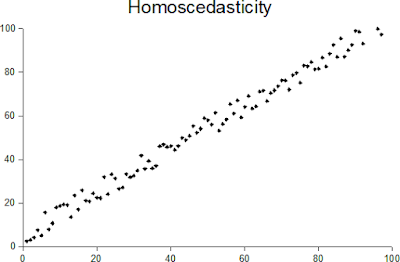
Homoscedasticity and heteroscedasticity - two of the scariest sounding terms in all of Statistics! So what do they mean? When one calculates the variance or standard deviation of a dataset of random variables, one assumes that the variance is constant across the entire population. This assumption is homoscedasticity. The opposite of this assumption is heteroscedasticity. In other words, a collection of random variables is heteroscedastic if there are sub-populations within the dataset that have different variances from others (source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heteroscedasticity). Another way of describing homoscedasticity is constant variance and another way of describing heteroscedasticity is variable variance. Jeremy J Taylor in his blog provides a great example of a distribution that is heteroscedastic. In his example, the independent variable is "age" and the predictor variable is "income". The example dis...
